code for article pfeilbr/aws-ses-playground
learn Simple Email Service (Amazon SES)
Notes
- send or receive emails
- verify domain (DNS txt) and/or email addresses (confirmation email) - verify that you own the email address or domain that you plan to send from
- understand Service quotas
- max message size - 10 MB per message (after base64 encoding).
- sending identity - domain or an email address
- send emails via SMTP or API (AWS CLI, AWS SDK)
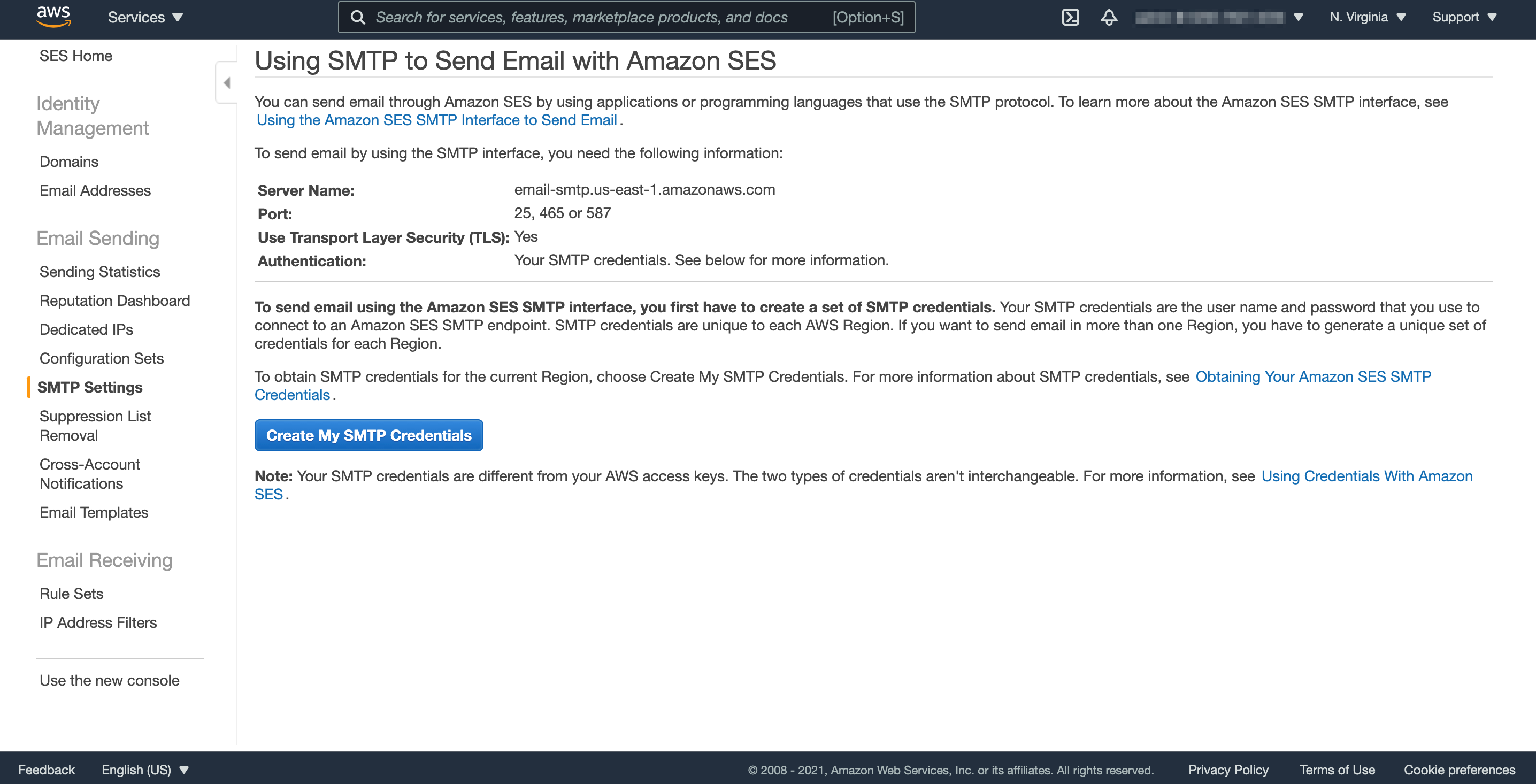
- connect to a URL that provides an endpoint for the Amazon SES API or SMTP interface (e.g. email-smtp.us-east-1.amazonaws.com:587)
- DKIM support - DKIM works by adding a digital signature to the headers of an email message. This signature can then be validated against a public cryptographic key that is located in the organization’s DNS record
- SPF support - SPF establishes a method for receiving mail servers to verify that incoming email from a domain was sent from a host authorized by that domain’s administrators. TXT record
"v=spf1 include:amazonses.com ~all" - IAM to control user access to email sending (e.g.
ses:SendEmail) - Configuration sets - groups of rules that you can apply to the emails you send using Amazon SES. can publish email sending events to CWL, Firehose, SNS
- Event types - Send, Reject, Delivery, Bounce, Complaint, Click Open Rendering Failure
- store inbound emails in S3
- trigger lambdas based on inbound emails
- publish your email sending events to CWLs or kinesis firehose
- Sending personalized email via email templates. templates contain placeholder values. based on Handlebars template system
- list management
- customers can manage their own mailing lists, known as contact lists.
- can create topics, associate topic preferences to a contact and specify
OPT_[IN|OUT]for the topic.
- Global Suppression List
- includes a global suppression list. When any Amazon SES customer sends an email that results in a hard bounce, Amazon SES adds the email address that produced the bounce to a global suppression list. The global suppression list is global in the sense that it applies to all Amazon SES customers. In other words, if a different customer attempts to send an email to an address that’s on the global suppression list, Amazon SES accepts the message, but doesn’t send it, because the email address is suppressed.
- enabled by default for all Amazon SES accounts. You can’t disable it.
- reputation dashboard to track bounce and complaint rates
- Dedicated IP Addresses
- IP pool management – If you lease dedicated IP addresses to use with Amazon SES, you can create groups of these addresses, called dedicated IP pools. You can then associate these dedicated IP pools with configuration sets
- SES sandbox - all new accounts.
- only send mail to verified email addresses and domains
- only send mail from verified email addresses and domains
- send a maximum of 200 messages per 24-hour period
- send a maximum of 1 message per second
- need to request production access to move out of sandbox
- VPC endpoint support - see New – Amazon Simple Email Service (SES) for VPC Endpoints
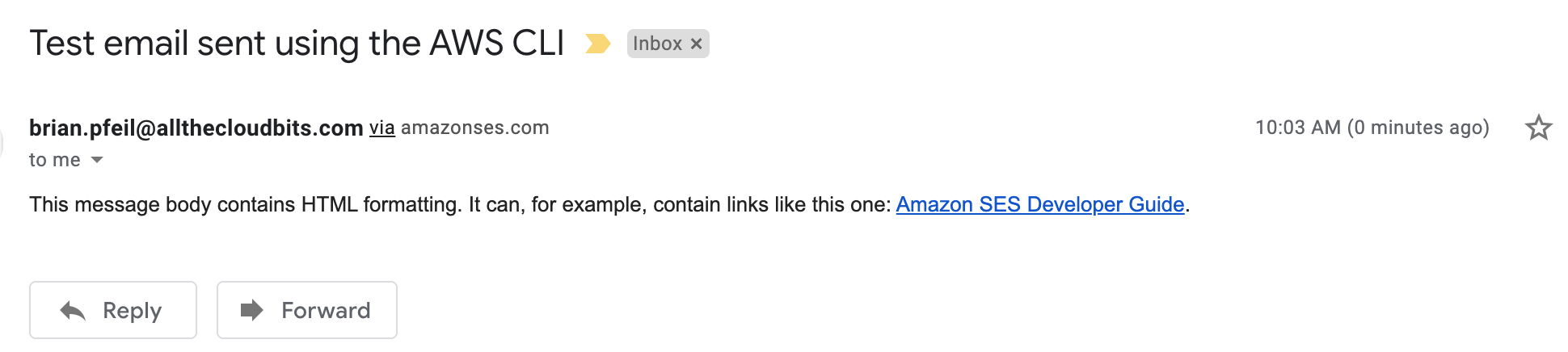
Send Email Using API
create destination.json and message.json files
# send email
# NOTE: cli security principal must have `ses:SendEmail` permission
aws ses send-email \
--from 'brian.pfeil@allthecloudbits.com' \
--destination file://destination.json \
--message file://message.json
# output/response
# {
# "MessageId": "010001788372bd22-b3d9950b-8310-43bf-bef3-256917951097-000000"
# }
Using SMTP interface
Create SMTP Credentials
Creates IAM user arn:aws:iam::529276214230:user/ses-smtp-user.20210330-092121 with following policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "ses:SendRawEmail",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Send Email using SMTP
# Testing your connection to the Amazon SES SMTP interface
openssl s_client -crlf -quiet -starttls smtp -connect email-smtp.us-east-1.amazonaws.com:587
# base64 encode creds
SMTP_USERNAME=$(echo -n "SMTPUsername" | openssl enc -base64)
SMTP_PASSWORD=$(echo -n "SMTPPassword" | openssl enc -base64)
# create SMTP email
# see `smtp-email-example.txt`
# send email
openssl s_client -crlf -quiet -starttls smtp -connect email-smtp.us-east-1.amazonaws.com:587 < smtp-email-example.txt
Twitter • Reddit